Course 736 Introduction to Process Safety Management Course 736 This page inten
Course 736 Introduction to Process Safety Management Course 736 This page intentionally blank Course 736 OSHAcademy Course 736 Study Guide Introduction to Process Safety Management Copyright © 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. No portion of this text may be reprinted for other than personal use. Any commercial use of this document is strictly forbidden. Contact OSHAcademy to arrange for use as a training document. This study guide is designed to be reviewed off‐line as a tool for preparation to successfully complete OSHAcademy Course 736. Read each module, answer the quiz questions, and submit the quiz questions online through the course webpage. You can print the post‐quiz response screen which will contain the correct answers to the questions. The final exam will consist of questions developed from the course content and module quizzes. We hope you enjoy the course and if you have any questions, feel free to email or call: OSHAcademy 15220 NW Greenbrier Parkway, Suite 230 Beaverton, Oregon 97006 www.oshatrain.org instructor@oshatrain.org +1.888.668.9079 Disclaimer This document does not constitute legal advice. Consult with your own company counsel for advice on compliance with all applicable state and federal regulations. Neither Geigle Safety Group, Inc., nor any of its employees, subcontractors, consultants, committees, or other assignees make any warranty or representation, either express or implied, with respect to the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of the information contained herein, or assume any liability or responsibility for any use, or the results of such use, of any information or process disclosed in this publication. GEIGLE SAFETY GROUP, INC., DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Taking actions suggested in this document does not guarantee that an employer, employee, operator or contractor will be in compliance with applicable regulations. Ultimately every company is responsible for determining the applicability of the information in this document to its own operations. Each employer’s safety management system will be different. Mapping safety and environmental management policies, procedures, or operations using this document does not guarantee compliance regulatory requirements. Revised: August 8, 2017 This page intentionally blank Course 736 Contents Course Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 1 The purpose for Process Safety Management (PSM) ................................................................. 1 Module 1: Why We Have Process Safety Management ................................................................. 2 The Problem ................................................................................................................................ 2 A Disastrous Record .................................................................................................................... 2 OSHA responds ........................................................................................................................... 4 The Clean Air Act Amendments and the PSM Standard ............................................................. 4 OSHA’s Final PSM Standard ........................................................................................................ 4 What are the benefits of an effective PSM program? ................................................................ 5 Module 1 Quiz ............................................................................................................................. 6 Module 2: How the PSM Standard Applies..................................................................................... 8 Application .................................................................................................................................. 8 What is a “process”? ................................................................................................................... 8 What industries does PSM target? ............................................................................................. 8 What does the employer need to develop? ............................................................................... 9 What is the impact of the PSM? ................................................................................................. 9 What can employers do to reduce risk? ..................................................................................... 9 Who is not covered by the PSM Standard? .............................................................................. 10 Module 2 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 11 Module 3: The PSM 14 Elements .................................................................................................. 13 Process Safety Information ....................................................................................................... 13 Hazards of the Chemicals Used in the Process ......................................................................... 13 Course 736 Technology of the Process ........................................................................................................ 14 Block Flow Diagrams ................................................................................................................. 15 Process Flow Diagrams ............................................................................................................. 16 Equipment in the Process ......................................................................................................... 16 Module 3 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 19 Module 4: Process Hazard Analysis .............................................................................................. 21 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. 21 Questions to consider when deciding the methods used in PHA’s .......................................... 21 Limitations of PHA Methods ..................................................................................................... 22 Prioritizing PHA’s ....................................................................................................................... 22 Methods for Conducting the PHA ............................................................................................. 22 The PHA ..................................................................................................................................... 23 Employer Response to PHA Team Findings .............................................................................. 25 Review and Revalidation ........................................................................................................... 25 Module 4 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 26 Module 5: Operating Procedures ................................................................................................. 28 What are operating procedures? .............................................................................................. 28 What must operating procedures describe? ............................................................................ 28 Elements of the Operating Procedures .................................................................................... 29 Module 5 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 32 Module 6: Employee Participation and Training .......................................................................... 34 Employers duty to involve employees ...................................................................................... 34 Course 736 Initial Training ........................................................................................................................... 34 Refresher Training ..................................................................................................................... 35 Training Documentation ........................................................................................................... 35 Module 6 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 36 Module 7: Contractors .................................................................................................................. 38 Application ................................................................................................................................ 38 Employer Responsibilities ......................................................................................................... 38 Contract Employer Responsibilities .......................................................................................... 39 Pre‐Startup Safety Review ........................................................................................................ 39 Module 7 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 41 Module 8: Mechanical Integrity and Hot Work Permit ................................................................ 43 Mechanical Integrity ................................................................................................................. 43 Training ..................................................................................................................................... 43 Inspection and Testing .............................................................................................................. 43 Equipment Deficiencies and Quality Assurance ....................................................................... 44 Hot Work Permit ....................................................................................................................... 44 Optional Exercise ...................................................................................................................... 45 Module 8 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 46 Module 9 – MOC, Investigation, Emergency Response and Trade Secrets .................................. 48 Management of Change (MOC) ................................................................................................ 48 Incident Investigation ............................................................................................................... 49 Emergency Planning and Response .......................................................................................... 50 Course 736 Compliance Audits .................................................................................................................... 50 Trade Secrets ............................................................................................................................ 51 The Future of PSM .................................................................................................................... 52 Final words of PSM wisdom! .................................................................................................... 52 Module 9 Quiz ........................................................................................................................... 54 Course 736 Copyright © 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. Page 1 of 55 Course Introduction The purpose for Process Safety Management (PSM) The major purpose of process safety management (PSM) of highly hazardous chemicals is to prevent unwanted releases of hazardous chemicals, especially into locations that could expose employees and others to serious hazards. OSHA simply states a hazardous chemical is any chemical which is a physical hazard or a health hazard. An effective process safety management program requires a systematic approach to evaluating the whole chemical process. Using this approach, the process design, process technology, process changes, operational and maintenance activities and procedures, non‐routine activities and procedures, emergency preparedness plans and procedures, training programs, and other elements that affect the process are all considered in the evaluation. This course is intended to introduce you to the basic requirements in OSHA standard CFR 1910.119, Process Safety Management of Highly Hazardous Chemicals, the need for process safety, and the tools used to implement process safety management systems. It covers the 14 elements required by the standard and some of the tools used to address process safety requirements, identify hazards, and manage risks. This course does not itself alter or determine compliance responsibilities, which are set forth in OSHA standards themselves and the Occupational Safety and Health Act. Special thanks go out to the U.S. Dept. of Labor, OSHA, for the content and images within this course. Course 736 Copyright © 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. Page 2 of 55 Module 1: Why We Have Process Safety Management The Problem Unexpected releases of toxic, reactive, or flammable liquids and gases in processes involving highly hazardous chemicals have been reported for many years. Incidents continue to occur in various industries that use highly hazardous chemicals which may be toxic, reactive, flammable, or explosive, or may exhibit a combination of these properties. Regardless of the industry that uses these highly hazardous chemicals, there is a potential for an accidental release any time they are not properly controlled. This, in turn, creates the possibility of disaster. Recent major disasters include: The 1984 Bhopal, India, incident resulting in more than 2,800 deaths. The October 1989 Phillips Petroleum Company, Pasadena, TX, incident resulting in 23 deaths and 132 injuries. The December 2005 Texas City Refinery explosion with 100 employees injured and 15 confirmed dead. The February 2010 Connecticut power plant explosion which resulted in 27 injuries and five deaths. The August 26, 2012 Amuay Oil Refinery explosion in Venezuela that wounded dozens and killed at least 39 people, including one child. A Disastrous Record Several major disasters involving highly hazardous chemicals drew international attention to the potential for major catastrophes; the public record in the U.S. is replete with information concerning many other less notable releases of highly hazardous chemicals. Hazardous chemical releases continue to pose a significant threat to employees and provide impetus, internationally and nationally, for authorities to develop or consider developing legislation and regulations to eliminate or minimize the potential for such events. Course 736 Copyright © 2017 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. Page 3 of 55 Methyl Isocyanate Tank Rupture and Release Bhopal, India – Dec. 2‐3, 1984 On the night of December 2‐3, 1984, a sudden release of about 30 metric tons of methyl isocyanate (MIC) occurred at the Union Carbide pesticide plant at Bhopal, India. The accident was a result of poor safety management practices, poor early warning systems, and the lack of community preparedness. The accident led to the death of over 2,800 people (other estimates put the immediate death toll as high as 8000) living in the vicinity and caused respiratory damage and eye damage to over 20,000 others. At least 200,000 people fled Bhopal during the week after the accident. Estimates of the damage vary widely between $350 million to as high as $3 billion. See the Chemical Safety Board video: Reflections on Bhopal After Thirty Years. Phillips 66 Houston Chemical Complex Pasadena, Texas – Oct. 23, 1989 On October 23, 1989, at approximately 1:00 p.m., an explosion and fire ripped through the Phillips 66 Company Houston Chemical Complex in Pasadena, Texas. Twenty‐ three workers were killed and more than 314 were injured. Property damage was nearly three‐quarters of a billion dollars.
Documents similaires

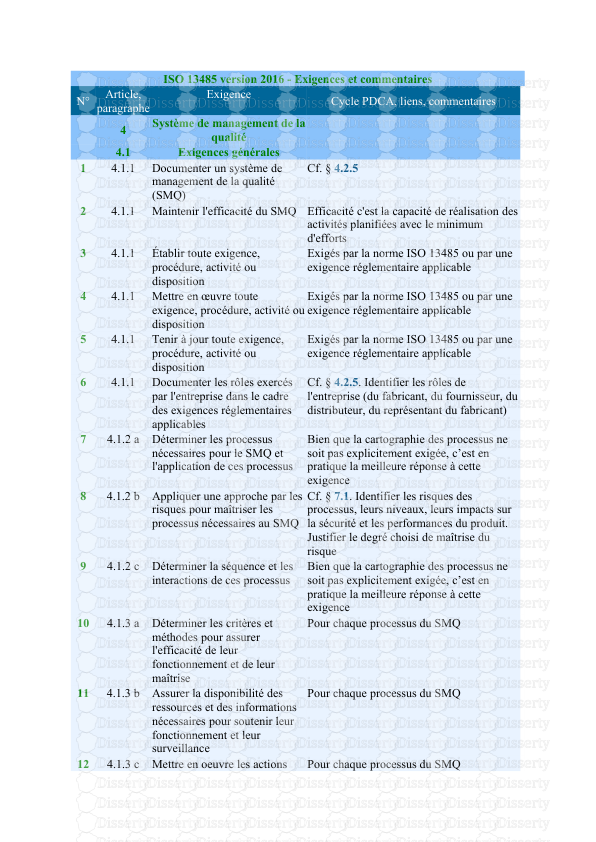








-
25
-
0
-
0
Licence et utilisation
Gratuit pour un usage personnel Attribution requise- Détails
- Publié le Jan 09, 2022
- Catégorie Administration
- Langue French
- Taille du fichier 1.4557MB


